Field of vision
It refers to the total area in which objects can be seen in side (peripheral) vision, while you focus your eyes on a central point.
This article describes the test that measures your visual field.
How the test is performed
Visual field confrontation test. It is a basic and quick review of the visual field. The health care provider sits directly in front of you. You will cover one eye and stare straight ahead with the other. You will be asked to say when you can see the examiner’s hand.
Goldmann’s Tangent Screen or Visual Field Examination You should sit approximately 3 feet away from a black cloth flat screen with an object in the center. You are asked to stare at the object in the center and let the examiner know when you can see an object moving toward your side vision. Usually the object is a pin or bead on the end of a black bar that the examiner moves. This test creates a 30-degree map of your central vision. This test is usually used to detect brain or nerve (neurological) problems.
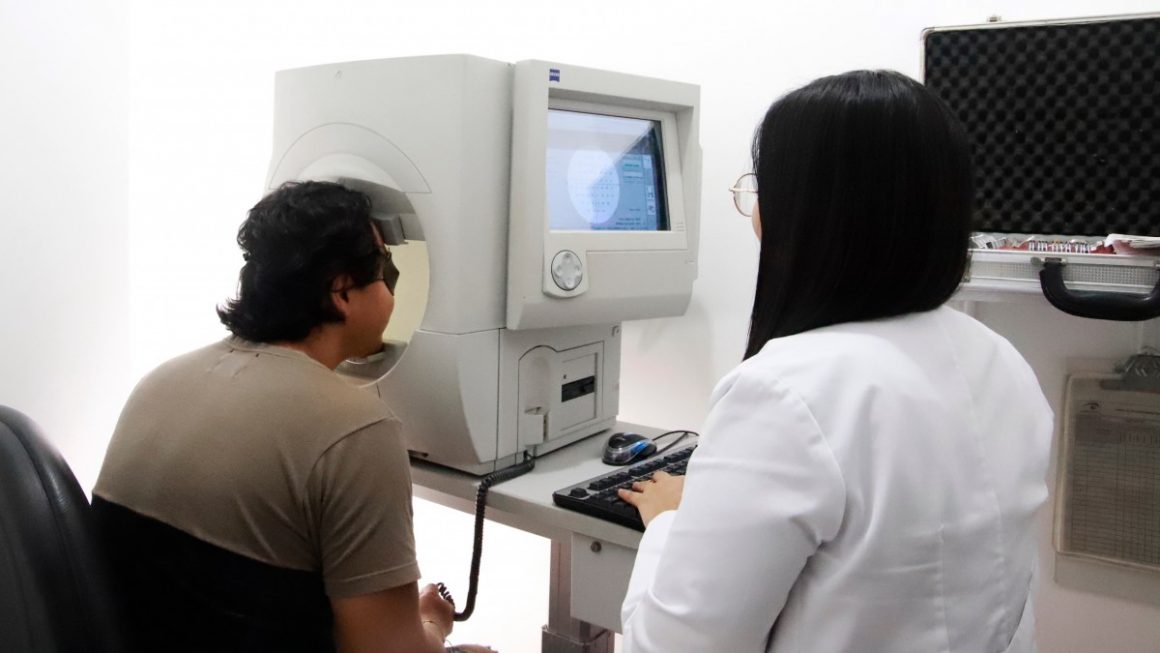
Goldmann perimetry and automated perimetry. For either of these exams, you sit in front of a concave dome and look at an object in the middle. You press a button when you see small flashes of light in your peripheral vision. In the Goldmann test, the flashes are controlled and projected by the examiner. In the automated exam, a computer controls and projects the flashes. Your answers help determine if you have a defect in your visual field. Both tests are often used to track conditions that may worsen over time.
Your provider will talk with you about the type of visual field exam you will have.